Many people who get HPV will not even realize it, since most types of HPV cause no visible signs or symptoms.
You may not be able to tell if you or your partner are infected, but just because you can’t see it, doesn’t mean that you’re not at risk.
Signs and symptoms of HPV-related cancer and warts
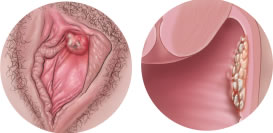
Genital warts
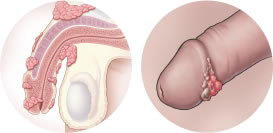
Genital warts are often the only visible sign that someone has an HPV infection. These are small growths that can appear on or inside the sex organs several weeks, months, or even years after sexual contact. They often look like small, red or white cauliflowers; they may be flat or feel like small raised bumps; and there may be only one that you can see or feel, or there could be many.
In women, genital warts can appear on the vulva, urethra, cervix, vagina, anus or thighs. In men, warts can appear on the penis, scrotum, anus or thighs. Genital warts are not a sign that you have cancer or that you will get cancer; they are not pre-cancerous.
Genital warts are usually painless but can sometimes cause itching or burning. When genital warts are visible, it can cause embarrassment and affect relationships because of reluctance to talk with your partner about it.
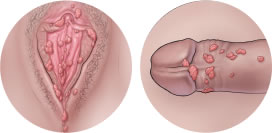
Cervical cancer
The signs and symptoms of cervical cancer can also be caused by other health conditions. It is important to discuss these with your doctor.
Some signs and symptoms of cervical cancer include abnormal vaginal bleeding, pain during sexual intercourse, increased discharge from the vagina, pain in the pelvic area or lower back, weight loss, lack of energy and shortness of breath.
A Pap test is a simple screening method that detects cell changes in your cervix. Regular Pap tests are the best way to find abnormal cervical cells early and treat them before they develop into cervical cancer.
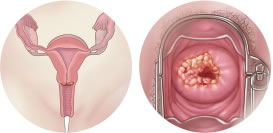
Anal cancer
Symptoms of anal cancer can include anal bleeding, difficulty passing stools, pain or lumps, itching or discharge. In the presence of signs and symptoms, an intra-anal examination should be performed.
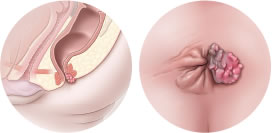
Penile cancer
Generally, penile cancer affects the head or foreskin of the penis rather than the shaft of the penis. Signs and symptoms can be a lump or ulcer on the penis. Growths can be raised, wart-like or flat and can be painful and inflamed. There may be itching and burning in the region as well.
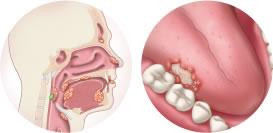
Head and neck (mouth and throat) cancer
Some typical symptoms of head and neck (mouth and throat) cancers include a lump or a sore in the head and neck area that does not heal, a sore throat that does not go away, white or red patches in the mouth, difficulty swallowing, and a change or hoarseness in the voice.
Vulvar and vaginal cancers
Often, there are no signs or symptoms for vulvar and vaginal cancers. If there are, they can appear as itching or burning that does not go away, pain in the pelvic area, abnormal vaginal bleeding, difficulty urinating, and/or painful intercourse. The Pap test does not screen for vulvar or vaginal cancers.